Serving Aerospace, Aviation and Automotive Industries with High-Performance Preforms and Components
We understand that exploring all aspects of our carbon matrix applications can be complex, so we’ve organized everything into easy-to-navigate sections. Use the content directory below to jump straight to the information you’re looking for.
At CMCMAT, we’re proud to offer a full range of Carbon Matrix composite customization services. With our advanced facilities and experienced team, we ensure that every client’s needs are met with the highest level of precision and quality. Here’s what we can offer you:

Both carbon-carbon composites and carbon-ceramic composites play crucial roles in a wide range of industries, thanks to their outstanding mechanical properties, thermal stability, wear resistance, and lightweight nature. The aerospace, automotive, and defense industries are the primary fields that rely on these composites, but their applications extend across many sectors including energy, industrial, sports, electronics, and marine industries. As demand for high-performance materials continues to grow, the use of these advanced composites will only increase, providing durable, efficient, and innovative solutions to modern challenges
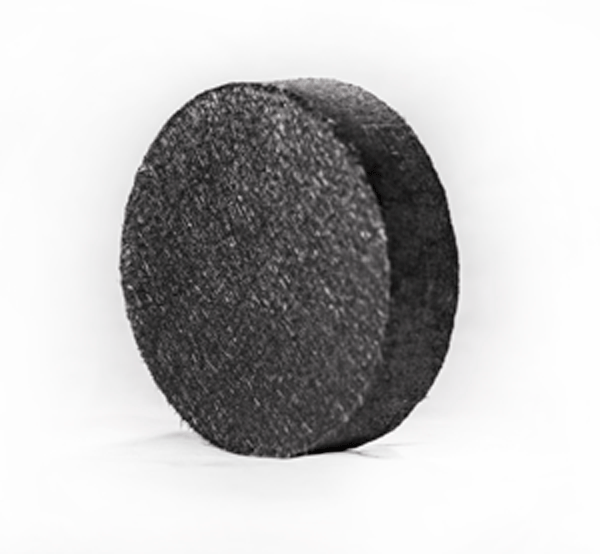

CMCMAT specializes in supplying 2.5D/3D structural preforms, directly fabricated from continuous fibers. By utilizing diverse fiber types, we tailor preform geometries to meet specific requirements. These high-performance preforms serve critical applications across industries such as automotive, aerospace, aviation, and thermal management systems, including: high-temperature resistant components; thermal insulation solutions; brake material blanks; advanced industrial composites.

Our high-density Carbon Carbon composites are engineered for the most demanding aerospace and industrial applications. By utilizing advanced chemical vapor infiltration (CVI) and pitch impregnation processes, we provide materials with exceptional mechanical properties and low erosion rates.
Specifically designed for rocket motor nozzles, throat inserts, and high-temperature structural components, our C/C materials offer the perfect balance of lightweight performance and extreme durability. Whether you require standard blocks or custom-machined parts, we deliver precision-engineered solutions to withstand the world’s harshest thermal environments.
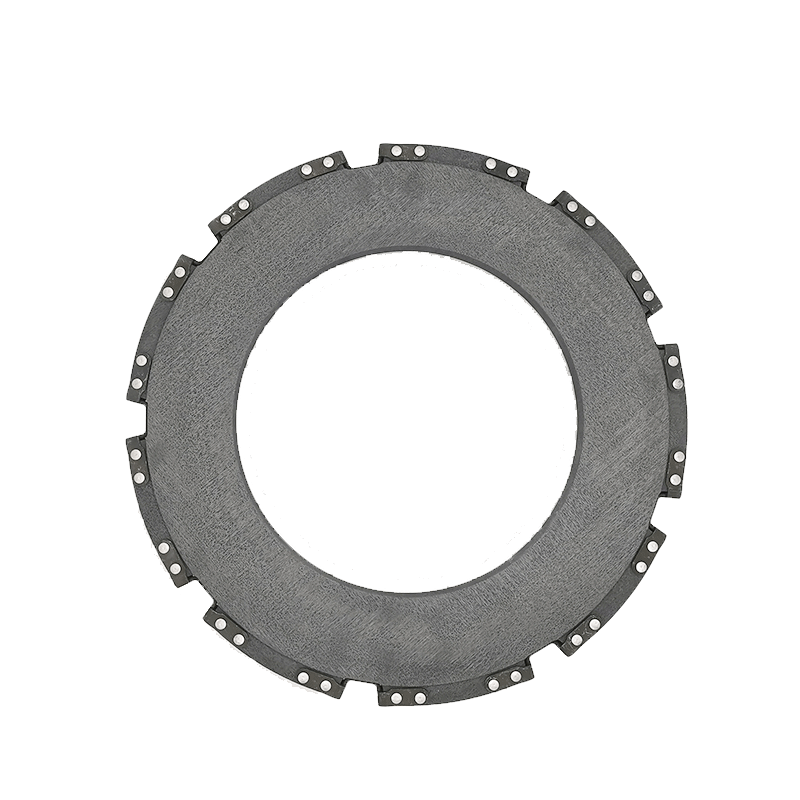
We offer a range of high-performance braking materials, including carbon-carbon (C/C), carbon-ceramic (C/SiC), and steel-based solutions. Select civil components are CAAC-PMA certified, ensuring compliance with stringent aviation safety standards. Designed for critical thermal management, our brakes deliver consistent performance across mission-critical aerospace and defense platforms, like UAV, civil planes and military jets.
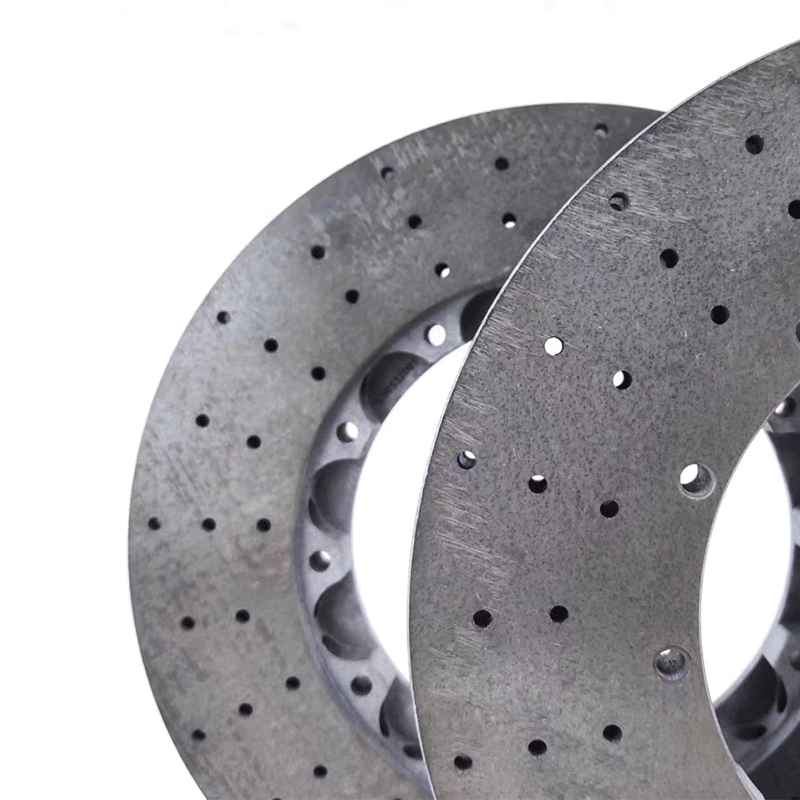

The automotive brakes we supplied are mainly carbon ceramic brakes. Carbon ceramic brakes are popular in track and street running. Customers can choose different brake pad compounds for different use.

Upgrade your stopping power with our advanced motorbike brake rotors. Designed for riders who demand zero brake fade and exceptional thermal management, our discs offer a significant weight reduction compared to traditional steel sinks, improving overall handling and unsprung weight.
Beyond rotors, we provide a complete performance ecosystem, including carbon-carbon clutch plates, and premium carbon-ceramic motorbike brake pads. Whether for the track or the street, our components deliver the ultimate in braking precision and reliability.

We have the ability to customize the carbon carbon or carbon ceramic applications based on your detailed requirments.
Here is the video how we develop the carbon carbon or carbon ceramic brake discs
CMCMAT is a premier carbon composite supplier specializing in high-performance materials designed for aerospace, defense, and automotive engineering. Our core expertise lies in the development of 3D carbon firber preforms and high-density carbon-carbon (C/C) composites.
Leveraging state-of-the-art CVI (Chemical Vapor Infiltration) and CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) processes, we produce materials that maintain exceptional structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 2500°C. Our product portfolio includes aircraft brake carbon carbon heat stacks for commercial and military aviation, as well as high-friction carbon ceramic brake rotors for the automotive racing industry.
As a dedicated supplier, we ensure that every component—from rocket nozzle throats to aircraft wheels and brakes spare parts—meets rigorous ISO quality standards. Whether you are sourcing for high-heat industrial applications or lightweight braking systems, CMCMAT provides the technical excellence required for the most demanding missions.
Answer: In vacuum or inert gas environments, our high-density carbon-carbon composites can withstand temperatures exceeding 2500°C (4532°F) while maintaining mechanical strength.
Answer: We provide aircraft brake carbon carbon heat stacks and steel brake components compatible with major platforms including Boeing, Airbus, and various military transport aircraft.
Answer: Carbon ceramic rotors offer up to 70% weight reduction, zero thermal fade, and significantly longer service life compared to steel, making them ideal for high-performance racing and heavy-duty defense vehicles.
Composition: Carbon-carbon is a composite material consisting of carbon fiber reinforcement in a matrix of graphite. The entire structure is carbon, which is why it is referred to as carbon-carbon.
Properties:
Applications: Due to its high-cost and complex manufacturing process, it’s typically used in specialized applications such as aerospace (rocket nozzles, heat shields), motorsports, and military.
Composition: Carbon ceramic materials, or ceramic matrix composites, are made from silicon carbide ceramic reinforced with carbon fibers. They are manufactured through a process that combines carbon fiber with silicon to produce a material that offers the benefits of both ceramic and carbon.
Properties:
Applications: Primarily used in the automotive industry for brake discs and pads in high-performance and luxury vehicles due to their ability to provide superior braking performance with less wear and resistance to high temperatures.
Each type of material offers specific advantages that make it suitable for different applications, particularly where high performance and durability under extreme conditions are required.
Note: Your email information will be kept strictly confidential.